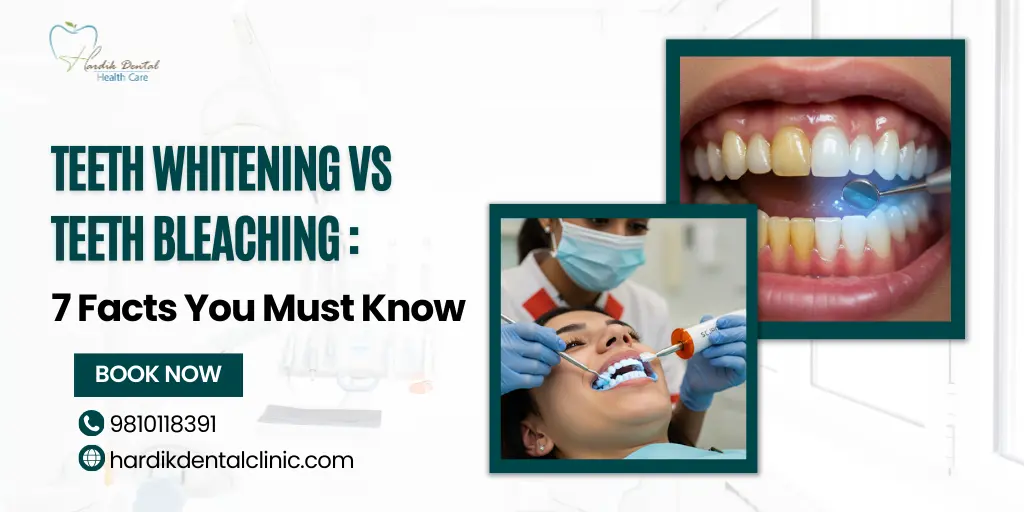
Introduction
When it comes to achieving a brighter smile, teeth whitening and bleaching are two popular options. Both methods lighten teeth, but they work in different ways. Understanding these differences is important so you can choose the best treatment for your needs. Want to see real patient results? Follow us on Instagram and Facebook for before-and-after transformations!
What is Teeth Whitening?
Teeth whitening refers to any process used to lighten the color of teeth. This can be achieved using various products, such as over-the-counter whitening toothpaste, at-home kits, or professional treatments at a dentist’s office. Teeth whitening usually targets surface stains caused by foods, drinks, or smoking.
What is Teeth Bleaching?
Teeth bleaching, on the other hand, uses stronger chemicals like hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide to lighten your teeth beyond their natural color. Bleaching works on deeper stains and can dramatically lighten your teeth, unlike whitening, which focuses more on surface stains.
Key Differences Between Whitening and Bleaching

The Process
- Whitening can be done with non-chemical products like whitening toothpaste or gels.
- Teeth bleaching requires peroxide-based products that penetrate deeper into the enamel.
Results
- Whitening typically lightens teeth by one or two shades.
- Teeth bleaching can lighten teeth several shades, depending on the strength of the peroxide used.
Safety of Whitening and Bleaching
Are They Safe?
Both teeth-whitening and teeth-bleaching are safe when used correctly. However, bleaching with hydrogen peroxide can sometimes lead to tooth sensitivity or gum irritation if not applied properly.
According to the American Dental Association (ADA), professional whitening is safe when done under expert supervision.
Professional vs. At-Home Treatments
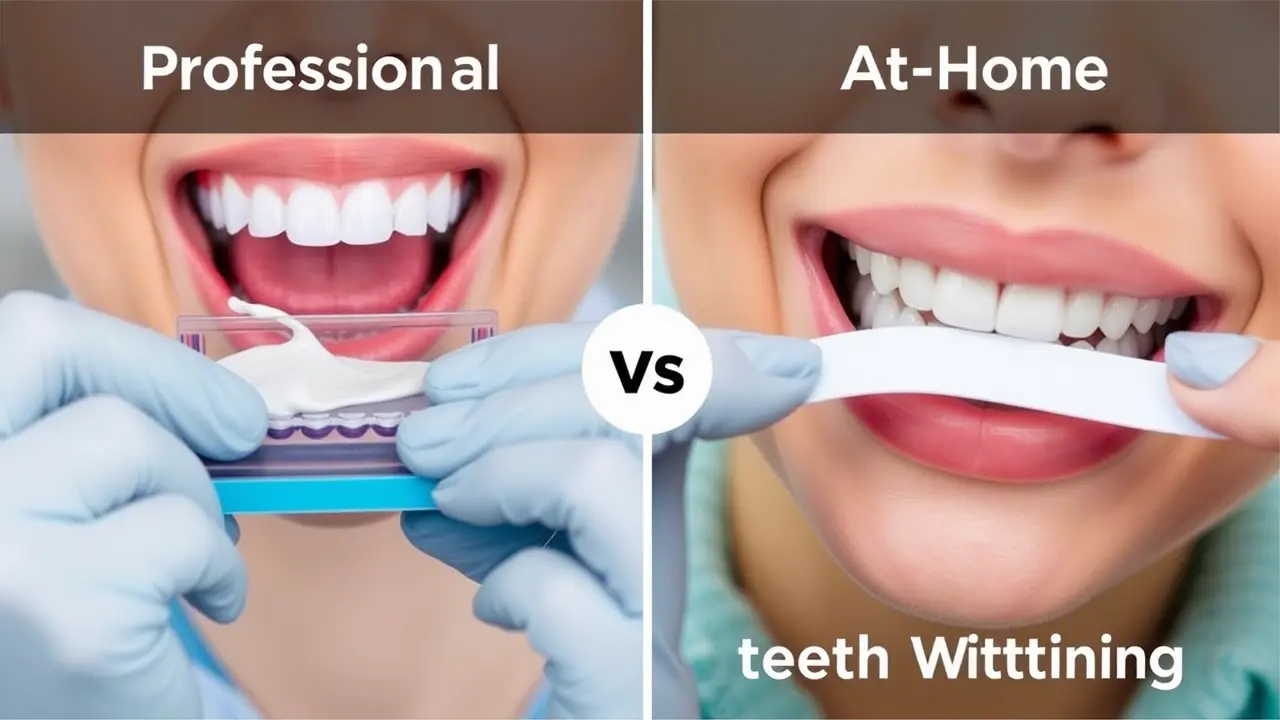
- Professional whitening and bleaching procedures at the dentist’s office are safer and more effective due to controlled application. Not sure which option is best for you? Chat with our dental experts on WhatsApp for a free consultation!
- At-home whitening products are less potent but can still effectively lighten surface stains.
Whitening Process
There are two main types of teeth whitening treatments: professional treatments at the dentist’s office and at-home kits. In both cases, the whitening process typically involves the use of peroxide-based agents. The most common ingredients are hydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide, which break down stains on the enamel.
Professional Teeth Whitening
In professional treatments, hydrogen peroxide is often used in higher concentrations (around 15% to 43%) to achieve quicker and more dramatic results. These treatments are typically more effective due to the controlled environment of a dentist’s office and the use of additional tools like light or heat to enhance the whitening process. For professional teeth-whitening treatments, visit our Service page.
At-Home Teeth Whitening
At-home kits also contain hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, but in lower concentrations (usually between 3% and 20%). These products take longer to show results, but they can still significantly improve the brightness of your teeth with consistent use.
Types of Teeth Whitening Methods
There are two main types of whitening methods: in-office treatments and at-home whitening kits. Each method has its own advantages, and the choice depends on your goals, budget, and how quickly you want results.
In-Office Teeth-Whitening
In-office whitening is often considered the most effective method. This treatment involves a stronger concentration of whitening agents like hydrogen peroxide. A dental professional uses specialised equipment, including light or heat, to speed up the whitening process. As a result, this method provides immediate and significant whitening, typically making your teeth several shades lighter in just one session. The controlled environment of a dental office also ensures that the procedure is safe and minimises risks like gum irritation or sensitivity.
At-Home Whitening
At-home teeth whitening products, such as whitening strips, trays, and toothpaste, are more affordable and convenient options. These kits are available over-the-counter and usually contain hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide in lower concentrations compared to professional treatments. While the results take longer to appear, at-home treatments can still effectively brighten your smile with consistent use over time. However, since these products are not applied by a professional, they may not be as strong or fast as in-office teeth whitening.
Benefits of Professional Treatment vs. DIY Kits
- In-office teeth whitening provides faster and more noticeable results. It uses stronger agents and professional equipment, so the results tend to be more dramatic.
- At-home whitening is a more budget-friendly and convenient option. While it may take longer to see noticeable changes, it’s a good choice for those looking for a less expensive alternative. Ready for a brighter smile? Book your appointment here and get expert dental whitening services!
How Does Teeth Whitening Work?
Understanding how whitening works can help you choose the right method for a brighter smile. The process involves breaking down stains on the surface of your teeth using peroxide-based bleaching agents. Depending on the treatment method, the strength of these whitening agents varies, affecting both the speed and effectiveness of the results.
The Science Behind Teeth-Whitening
The active ingredient in most whitening products is either hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These compounds release oxygen molecules, which penetrate the enamel and break down stain-causing compounds. This oxidation process helps lighten the tooth color, giving a whiter appearance.
At-Home Whitening vs. In-Office Whitening
- At-home teeth-whitening kits contain a lower concentration of hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, typically ranging from 3% to 20%. These include whitening strips, trays, gels, and toothpaste. Since the concentration is lower, results take longer to appear, but they are still effective with consistent use.
- In-office whitening treatments use stronger peroxide-based bleaching agents, often between 15% and 43%. Dentists may also use specialized LED lights or heat to accelerate the whitening process, producing faster and more dramatic results in just one session.
Factors That Affect Whitening Results
Several factors influence how well whitening works:
- Stain type: Surface stains from coffee, tea, and smoking respond better to whitening than do deep intrinsic stains.
- Enamel thickness: Thicker enamel can improve results, while thin enamel may make stains harder to remove.
- Treatment duration: The longer you use a peroxide-based whitening product, the greater the results—though higher concentrations should be used for shorter periods to avoid tooth sensitivity.
Pros and Cons of Teeth-Whitening
Choosing between whitening and bleaching treatments depends on your goals, budget, and tooth sensitivity. Both methods have benefits and drawbacks that should be considered before starting a treatment.
Pros of Teeth-Whitening
Teeth-whitening is gentle on the teeth, making it a safe option for most people. It can be done at home using whitening strips, gels, or toothpaste, providing a convenient way to brighten your smile without visiting a dentist. This method effectively removes surface stains caused by coffee, tea, and smoking. Many whitening products are also budget-friendly, making them an affordable choice for those looking to improve their smile gradually.
Cons of Teeth-Whitening
While effective for surface stains, teeth-whitening may take longer to show noticeable results. Over-the-counter treatments often require weeks of consistent use to achieve a significant difference. It is also limited in its effectiveness against deep intrinsic stains or discoloration caused by medications. Some individuals may experience mild tooth sensitivity after using peroxide-based whitening products, especially with frequent or prolonged use.
Pros and Cons of Teeth-Bleaching
Pros of Teeth Bleaching
Teeth bleaching provides faster results compared to whitening treatments. Professional bleaching done at a dentist's office can significantly lighten teeth in just one session. It is highly effective in removing deep intrinsic stains caused by aging or certain medications. Additionally, bleaching agents can whiten teeth beyond their natural shade, creating a brighter smile than what is possible with standard whitening methods.
Cons of Teeth Bleaching
Despite its effectiveness, teeth bleaching can lead to increased tooth sensitivity due to the use of stronger peroxide-based solutions. The higher concentration of bleaching agents may cause discomfort for individuals with sensitive teeth. In-office bleaching treatments are also more expensive than at-home whitening options, making them less accessible to some people. If not applied correctly, bleaching agents can irritate the gums and soft tissues, leading to temporary discomfort or inflammation.
How to Maintain Whiter Teeth After Whitening or Bleaching
Achieving a brighter smile with teeth-whitening or bleaching is just the beginning. Check out more expert tips on dental care in our blog section! To keep your teeth looking their best, it's essential to follow proper maintenance practices.
Avoid Staining Foods and Drinks
Certain foods and beverages can stain your teeth, dulling the effects of your whitening treatment. Drinks like coffee, tea, red wine, and soda can leave behind stains, while foods such as berries, tomato sauce, and soy sauce contribute to discoloration. Using a straw when drinking dark-colored beverages can minimize direct contact with your teeth and reduce staining.
Practice Good Oral Hygiene

Brushing your teeth at least twice a day using a whitening toothpaste helps remove surface stains before they settle. Flossing daily is also crucial to prevent plaque buildup, which can make teeth appear dull. For added protection, rinsing with an alcohol-free whitening mouthwash can help maintain brightness while keeping your mouth fresh.
Schedule Regular Dental Cleanings
Professional dental cleanings help remove plaque and tartar that can make teeth look yellow. Dentists use specialized tools to polish the enamel, enhancing the results of your whitening or bleaching treatment. Visiting your dentist every six months ensures that your teeth stay clean, healthy, and bright.
Use Touch-Up Treatments
Over time, teeth naturally lose their brightness. To maintain results, consider using touch-up whitening treatments, such as whitening strips or trays, every few months. Your dentist may also recommend in-office touch-up sessions to keep your teeth looking their best.
What Are the Risks of Teeth Whitening and Bleaching?
While teeth whitening and bleaching can enhance your smile, they are not without risks. Understanding these risks can help you make an informed decision before starting a treatment.
Tooth Sensitivity
One of the most common side effects of whitening treatments is tooth sensitivity. Peroxide-based bleaching agents temporarily weaken the enamel, exposing the dentin underneath. This can cause discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. Using desensitizing toothpaste can help alleviate sensitivity over time.
Gum Irritation
Some whitening and bleaching products can cause gum irritation, especially if the bleaching agent comes into direct contact with the soft tissues. This can result in redness, swelling, or a burning sensation. Ensuring that whitening trays fit properly and avoiding overuse of bleaching agents can reduce the risk of irritation.
Enamel Damage and Overuse Risks
Frequent application of tooth sensitivity treatments is likely to wear the enamel of your teeth down, thus bringing you to a condition of more susceptibility to decay and sensitivity. Whitening will damage and soften your teeth because of the high levels of peroxide contained in OTC products, should you use it beyond the necessary time. Complying with the given instructions on proper use not only is beneficial but also saves you from the worry of any persistent damages.
Importance of Consulting a Dentist
Before starting any whitening or bleaching treatment, it's best to consult a dentist, especially if you have dental restorations like crowns or veneers. Professional guidance ensures that the chosen method is safe and effective for your teeth. DIY whitening methods, such as using baking soda or lemon juice, can be abrasive and harmful to enamel, so professional recommendations should always be prioritized. "Stay updated with expert dental tips—connect with us on LinkedIn!"
Which is Better for You: Teeth-Whitening or Bleaching?
When choosing between teeth-whitening and bleaching, it's essential to consider your specific needs. Both methods aim to enhance the brightness of your smile, but they work in different ways and offer varying results.
Understanding the Difference
Whitening is mainly about the removal of surface stains resulting from food, drinks, and tobacco. The approach incorporates chemicals like hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which act as lighteners to remove stains and thus bring back the teeth's natural color. Teeth bleaching, on the other hand, goes beyond surface stains. It uses stronger peroxide-based solutions to lighten the actual shade of the teeth, making them whiter than their natural color. This method is ideal for deep discoloration caused by aging, medication, or excessive fluoride exposure.
Which Works Best for Your Stains?
- Whitening is best for extrinsic stains, which occur on the outer surface of the teeth due to coffee, tea, red wine, and smoking. It helps restore a brighter appearance but does not change the natural tooth shade.
- Bleaching is better for intrinsic stains, which develop inside the tooth due to aging, certain medications, or excessive fluoride. This method can make teeth several shades whiter.
Factors to Consider Before Choosing
- Cost
- Over-the-counter whitening products are more affordable and can be done at home.
- Professional bleaching treatments are more expensive but provide faster, longer-lasting results.
- Desired Results
- If you want a subtle improvement, whitening toothpaste or strips may be enough.
- If you want dramatic whitening, professional bleaching treatments can lighten teeth by multiple shades.
- Teeth Sensitivity
- Whitening products typically have lower peroxide concentrations, making them gentler on sensitive teeth.
- Bleaching treatments use higher peroxide levels, which may cause temporary sensitivity, especially in individuals with already sensitive teeth.
Which Option Should You Choose?
If you have minor stains and want gradual improvement, at-home whitening products may be suitable. However, if you have severe discoloration and want fast, noticeable results, professional bleaching might be the better option. Consulting a dentist can help determine the best treatment for your teeth type and sensitivity level. Want to see professional whitening in action? Watch our detailed YouTube videos to learn more!
Conclusion
Choosing between teeth-bleaching and teeth-whitening depends on the type of stains and your dental needs.
Whitening removes surface stains caused by food, drinks, and smoking. Teeth-bleaching works deeper and lightens teeth beyond their natural shade.
Cost, results, and sensitivity should be considered before making a choice. Over-the-counter whitening works for mild stains, while professional bleaching gives faster results.
Consulting a dentist is essential before any treatment. A professional can recommend the safest method and minimize risks like sensitivity and gum irritation.
For the best results and long-term whiteness, follow proper oral hygiene and avoid stain-causing foods and drinks.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, but it's best to use products for sensitive teeth and consult a dentist for guidance.
Results can last 6 months to 2 years, depending on diet and oral care.
Yes, but professional treatments provide faster and more noticeable results.
When done correctly, bleaching is safe. Overuse can cause sensitivity and weak enamel.
Whitening helps surface stains, while bleaching removes deeper discoloration.